Namaste BlockChain - by BlockSpirit
This article covers the knits and grits of blockchain basics. You can get an overview of the complex topics related to blockchain & Crypto.
Table of contents
🙏 Namaste🔗BlockChain 🙏
If you are a bit overwhelmed by the whole concept of Blockchain & Cryptocurrency, no worries you can get started by taking one step at a time, so here's the team BLOCKSPIRIT presenting the knits and grits of blockchain basics.

Who invented Bitcoin?
Amazingly, nobody knows who invented Bitcoin. We only know them by their screen name - Satoshi Nakamoto. Satoshi could be a single person, a group of programmers, or if you believe some of the weirder theories, a time-traveling alien or secret government team.Satoshi published a 9-page document in 2008, detailing how the Bitcoin system worked. Months later, in 2009, the software itself was released.- Web3 is decentralized: instead of large swathes of the internet controlled and owned by centralized entities, ownership gets distributed amongst its builders and users.
- Web3 is permissionless: everyone has equal access to participate in Web3, and no one gets excluded.
- Web3 has native payments: it uses cryptocurrency for spending and sending money online instead of relying on the outdated infrastructure of banks and payment processors.
- Web3 is trustless: it operates using incentives and economic mechanisms instead of relying on trusted third-parties.
What is Web3?
Web3 has become a catch-all term for the vision of a new, better internet. At its core, Web3 uses blockchains, cryptocurrencies, and NFTs to give power back to the users in the form of ownership. Instead of a Web monopolized by large technology companies, Web3 embraces decentralization and is being built, operated, and owned by its users. Web3 puts power in the hands of individuals rather than corporations. Before we talk about Web3, let's explore how we got here.
Core ideas of Web3
Web 1.0 VS Web 2.0 VS Web 3.0
Web 1.0
The first inception of Berners-Lee's creation, now known as 'Web 1.0', occurred roughly between 1990 to 2004. Web 1.0 was mainly static websites owned by companies, and there was close to zero interaction between users - individuals seldom produced content - leading to it being known as the read-only web.
Web 2.0
> If you're not paying for the product,You're the product
The Web 2.0 period began in 2004 with the emergence of social media platforms. Instead of a read-only, the web evolved to be read-write. Instead of companies providing content to users, they also began to provide platforms to share user-generated content and engage in user-to-user interactions. As more people came online, a handful of top companies began to control a disproportionate amount of the traffic and value generated on the web. Web 2.0 also birthed the advertising-driven revenue model. While users could create content, they didn't own it or benefit from its monetization. Web 2.0 is the age of targeted advertising and the lack of privacy for it's users.
Web 3.0- Read-Write-Own
> Privacy is in your hands
Web3 is supposed to be a more decentralised web that challenges the dominance of the tech giants by concentrating the power and data in the hands of the users, instead of the big tech corporations. This means that data is distributed across networks and no single entity owns the information. Web3 can power the new financial world order on ‘metaverse’ and unleash innovation in online gaming, tokenisation of assets in virtual spaces and empower users to exercise complete control over their identity and data.
What is a block?🅱
A blockchain network’s transactions are composed of sequential groups of data that are packaged together into “blocks” strung together linearly. Each block also contains a set of transaction data that is processed once the block is finalized. The individual blocks that make up the larger blockchain contain crucial information for the functioning of the network. Each new block contains cryptographically verifiable data regarding transactions, as well as a numerical challenge that must be completed in order for the current block to be approved and added to the blockchain.
What is blockchain?🅱⛓️
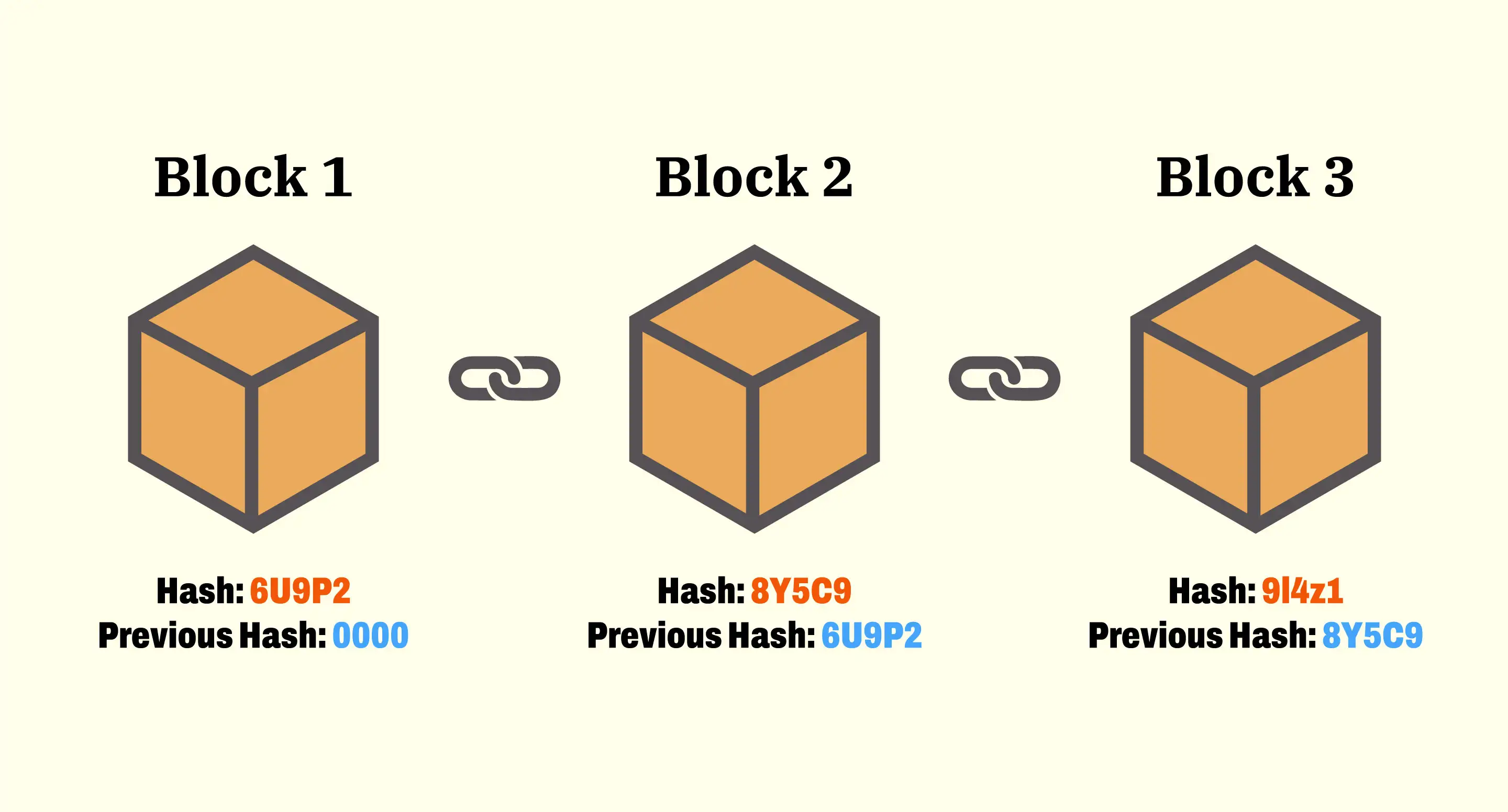
A blockchain is a distributed database or ledger that is shared among the nodes of a computer network. As a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in digital format. Blockchains are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems, such as Bitcoin, for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions. The innovation with a blockchain is that it guarantees the fidelity and security of a record of data and generates trust without the need for a trusted third party. One key difference between a typical database and a blockchain is that a database usually structures its data into tables, whereas a blockchain, as its name implies, structures its data into chunks (blocks) that are strung together. This data structure inherently makes an irreversible timeline of data when implemented in a decentralized nature. When a block is filled, it is set in stone and becomes a part of this timeline. Each block in the chain is given an exact timestamp when it is added to the chain.
> Key Takeaways 1. Blockchain is a type of shared database that differs from a typical database in the way that it stores information, blockchains store data in blocks that are then linked together via cryptography. 2. As new data comes in, it is entered into a fresh block. Once the block is filled with data, it is chained onto the previous block, which makes the data chained together in chronological order. 3. Different types of information can be stored on a blockchain, but the most common use so far has been as a ledger for transactions. 4. In Bitcoin’s case, blockchain is used in a decentralized way so that no single person or group has control, rather all users collectively retain control. 5. Decentralized blockchains are immutable, which means that the data entered is irreversible. For Bitcoin, this means that transactions are permanently recorded and viewable to anyone.
What is a hashing function
A hashing function is a system where you can put something into it, and it’ll output a hash. There’s a ton of math happening inside this “magical black box”, but essentially you give it something and it gives you something. In this case, bitcoin uses SHA-256 hashing function. SHA stands for “Secure Hashing Algorithm” and 256 refers to the amount of 0 and 1s that it has in whatever it puts out. Whether you put it your name or the entire dictionary, it’ll always be 256 1s and 0s. Our computers are smart and so they convert those 0 and 1s to letters and numbers.
What is a Crypto currency 💱

A cryptocurrency is a form of digital asset based on a network that is distributed across a large number of computers. This decentralized structure allows them to exist outside the control of governments and central authorities.
OR
A digital currency that is secured by cryptography and is, typically, used as a medium of exchange within a peer-to-peer (P2P) digital economic system. The use of cryptographic techniques is what ensures that these systems are completely immune to fraud and counterfeiting
### Types of Cryptocurrency
1. Bitcoin
2. Ether (Ethereum)
3. Tether
4. Binance Coin
What is a Crypto wallet 👛

Crypto wallets store your private keys, keeping your crypto safe and accessible. They also allow you to send, receive, and spend cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. ### Why are crypto wallets important? Unlike a normal wallet, which can hold actual cash, crypto wallets technically don’t store your crypto. Your holdings live on the blockchain, but can only be accessed using a private key. Your keys prove your ownership of your digital money and allow you to make transactions. If you lose your private keys, you lose access to your money. That’s why it’s important to keep your hardware wallet safe, or use a trusted wallet provider like Coinbase.
Learn more about walletsWhat is Proof Of Work?
PoW or proof of work is a special protocol that aims to deter cyber-attacks such as DDoS (distributed denial-of-service attacks), which can use up the resources of a computer stem with the help of multiple fake requests. It uses a trustless and distributed consensus system. PoW implements a decentralized system and works without needing a central authority. The PoW consensus mechanism can verify transactions without needing a third party. PoW makes double-spending difficult by proving that every user has done several computations. Many other blockchain projects that copied the original Bitcoin code also follow the Proof of Work model.
### How Does PoW Work?
Proof of work requires an expensive computer calculation or, in other words, the process of mining. Mining needs to be performed to create trustless transactions on the blockchain.
Step 1) Transactions are compiled and bundled up together in the form of a block. Step 2) Miners then verify transactions within each block, checking to see if they are legitimate. Step 3) Miners then solve a mathematical puzzle known as a proof of work problem to proceed. All miners have to compete. Step 4) The first miner who solves each block problem is rewarded. Step 5) The verified transactions are then stored on the blockchain.> makes it expensive to cheat, but profitable to act honestly
In Proof-of-work any block that includes an invalid transaction will be automatically rejected by the network. It’s expensive for you to even attempt to cheat. You’ll waste your own resources without any reward.
### Advantages of PoW
- Proof-of-Work was invented to stop double-spending attempts.
- It is one of the most secure consensus mechanisms.
- Cryptos based on PoW has more mining power and are more secure.
- Mining earns rewards in a typical PoW model.
- Proof of work is random yet fair.
### Proof of work examples
Proof of work model has existed for a long time so let us go through some examples of PoW. Emails The first example we shall explore is emails attached with a lengthy piece of text. Ordinary computers can send millions of emails per day, but executing other tasks and receiving a lot of spam can affect its efficiency and reduce processing costs. PoW is used to lower processing cycles by providing complex computation problems which enhance security. Cryptocurrencies One of the most famously used examples of PoW is mining a cryptocurrency. The PoW model ensures that miners have direct authority within the network. It also prevents double-spending attacks from occurring. Miners have a fixed income because PoW includes enough headers in new blocks. DDoS Another example of PoW is migrating DDoS attacks that cause inconvenience and disruptions. The PoW algorithm solves complex mathematical problems by getting a collective solution. PoW helps to solve problems in a distributed sort of way. This way, even a small number of participants can solve complex problems.
What is Proof Of Stake?

In the case of proof of work, that cost is computing power.This requires an enormous amount of computing power and, thus, electricity. Ethereum uses 113 terawatt-hours per year—as much power as the Netherlands, according to Digiconomist. A single Ethereum transaction can consume as much power as an average US household uses in more than a week. Bitcoin’s energy consumption is even worse. Proof of stake (PoS) is a type of consensus mechanism which is used to validate transactions on the blockchain. It works by allowing cryptocurrency owners to stake their coins. This gives them the right to verify new blocks of transactions on the blockchain and add them to the network. An algorithm selects from a pool of validators based on the amount of funds they have locked up. The more you stake, the greater your chance of “winning the lottery.” If you’re chosen and your block is accepted by a committee of “attestors”—a group of validators randomly chosen by an algorithm—you are awarded newly minted ether.
### How Does PoS Work?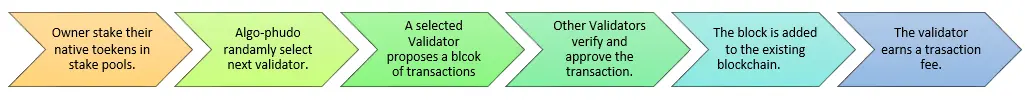
In theory, PoS is an “ideal” solution for scaling problems within the PoW mechanism. Ethereum 2.0 will be 100% proof-of-stake. Hence it will process its transactions, NFT transactions, and execute smart contract transactions.
Step 1) Users who own native tokens of a blockchain store all or a part of it in staking pools safely. Step 2) The algorithm pseudo-randomly chooses the next validator in line. Step 3) The chosen validator has to propose a block and the number of transactions in it. Step 4) Other participants get to approve and verify the proposed transaction. Step 5) A new block is added to the blockchain. Step 5) The selected validator earns a transaction fee.> Everyone is equal
The Proof-of-Work model has become an unfair system where common participants have no chance of getting the mining rewards. But the same is not true for proof-of-stake, where everyone gets an equal opportunity to become a forger and get rewards.
### Advantages of PoS
- The PoS mechanism is safe from 51% of attacks.
- The Proof-of-stake does not need expensive hardware for processing.
- Transactions are faster and relatively inexpensive.
- Processing in the case of PoS does not use much energy.
- Stakes act as a financial motivator in the PoS model.
### Proof of Stake Examples
Proof-of-Stake is the so-called better way of solving cryptographic problems. Following are a few cryptocurrencies that use the PoS model that is faster and more secure than PoW. Tezos: The decentralized network of Tezos includes an incentive mechanism that rewards validators. For maintaining and securing the network, validators receive newly-created tokens. Stakes increase as new participants enter the network and become active. The PoS system in Tezos also protects rewards and blockchain data from tampering. Ethereum 2.0: The co-founder of Ethereum, Vitalik Buterin, proposed the Ethereum Improvement Proposal in 2016. It uses a modified version of the PoW algorithm called Sharding. The concept of Sharding can improve network performance by holding more hash power. Sharding would also increase the number of transactions in a block. Cosmos: Cosmos is popular for deploying a PoS network for widespread use (more than Bitcoin). By securing millions of users, the project hopes to become the largest PoS-based coin. Its target audience includes people who do not have access to the banking system.
What is Fiat Currency?💵
Simply put, fiat currency is legal tender that derives its value from its issuing government rather than a physical good or commodity. The strength of the government that establishes the value of fiat currency is key in this type of money. Most countries around the world use the fiat currency system to purchase goods and services, invest, and save. Fiat currency replaced the gold standard and other commodity-based systems in establishing the value of legal tender.
What is a NONCE?🔢
A nonce refers to a number or value that can only be used once. Nonces are often used on authentication protocols and cryptographic hash functions. In the context of blockchain technology, a nonce refers to a pseudo-random number that is utilized as a counter during the process of mining.
For instance, Bitcoin miners need to try and guess a valid nonce as they perform multiple attempts to calculate a block hash that meets certain requirements (i.e., that starts with a certain number of zeros). When competing to mine a new block, the first miner to find a nonce that results in a valid block hash is granted the right to add the next block into the blockchain - and is rewarded for doing so.
What is Ethereum Gas? ⛽
The concept of gas was introduced to compensate miners(Miners can be defined as accountants who record every transaction to the blockchain.) for their work done on maintaining and securing the blockchain. After the proof of stake algorithm was rolled out in September 2022, gas fees became the reward for staking ETH and participating in validation—the more a user has staked, the more they can earn. On the Ethereum platform, “gas” is a unit describing the amount of computational power needed to execute specific operations on the network. Gas is the fee required to successfully conduct a transaction or execute a contract on the Ethereum blockchain platform. Fees are priced in tiny fractions of the cryptocurrency ether (ETH)—denominations called gwei (10-9 ETH). Gas is used to pay validators for the resources needed to conduct transactions.
What is staking?
Staking has become a popular way for crypto investors to grow their holdings without having to sell their digital assets. Staking can be seen as the crypto equivalent of putting your funds in a savings account. The difference is that, when you deposit money in your savings account, the bank ends it out to others, sharing the interest with you. When you stake your crypto, you lock up your digital assets to participate in maintaining the security of a blockchain network, earning rewards in return.
What is Metamask?
The Metamask wallet is basically a crypto wallet that provides support for ETH-based tokens such as ERC-721 and ERC-20 tokens. It is available as a browser plugin that you can install easily, just like any other browser extension. Interestingly, you can enjoy a seamless connection to any Ethereum-based decentralized app after installing the Metamask Chrome extension or Firefox extension. You could easily access any decentralized application like yield farming protocols and NFT marketplaces with the wallet. With the facility of web browser integration in the form of plugins, you can have convenient experiences in the use of MetaMask. This is probably one of the foremost reasons for its rapidly increasing rates of adoption. As the demand for a decentralized web starts to gain momentum, MetaMask can serve as a gateway for you into a new world of exciting opportunities with dApps, web browsing, and DeFi, and blockchain technology. MetaMask is a bridge that allows you to visit the distributed web of tomorrow in your browser today. It allows you to run Ethereum dApps right in your browser without running a full Ethereum node.
What is Meta Mask🦊?
MetaMask is a free crypto wallet software that can be connected to virtually any Ethereum-based platform. The extension injects the Ethereum web3 API into every website's javascript context, so that dapps can read from the blockchain. MetaMask also lets the user create and manage their own identities (via private keys, local client wallet and hardware wallets like Trezor™), so when a Dapp wants to perform a transaction and write to the blockchain, the user gets a secure interface to review the transaction, before approving or rejecting it.
What are Smart Contracts?🤝
A "smart contract" is simply a program that runs on the Ethereum blockchain. It's a collection of code (its functions) and data (its state) that resides at a specific address on the Ethereum blockchain. Smart contracts are a type of Ethereum account. This means they have a balance and can be the target of transactions. However they're not controlled by a user, instead they are deployed to the network and run as programmed. User accounts can then interact with a smart contract by submitting transactions that execute a function defined on the smart contract. Smart contracts can define rules, like a regular contract, and automatically enforce them via the code. Smart contracts cannot be deleted by default, and interactions with them are irreversible.
What is Ethereum Merge?🔀
The Merge represents the joining of the existing execution layer of Ethereum (the Mainnet we use today) with its new proof-of-stake consensus layer, the Beacon Chain. It eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining and instead secures the network using staked ETH. This a truly exciting step in realizing the Ethereum vision – more scalability, security, and sustainability. After the blockchains merge, Ethereum will introduce sharding, a method of breaking down the single Ethereum blockchain into 64 separate chains, which will all be coordinated by the Beacon Chain. Shard chains will allow for parallel processing, so the network can scale and support many more users than it currently does. Many see the inclusion of shard chains as the official completion of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, but it’s not scheduled to happen until 2023. - Explore This

